
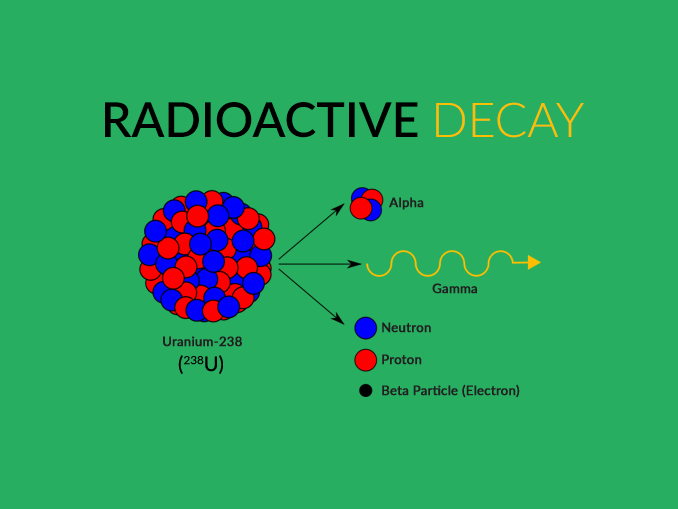
Radioactive element definition plus#
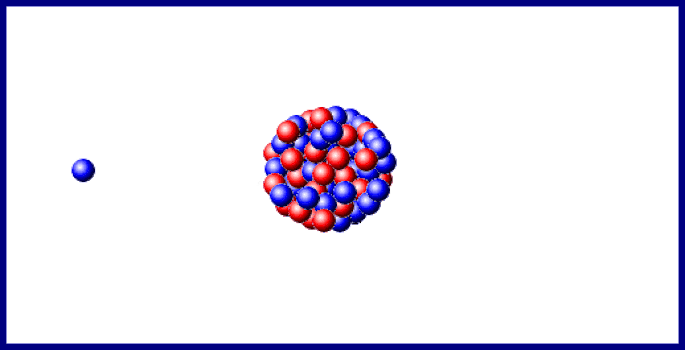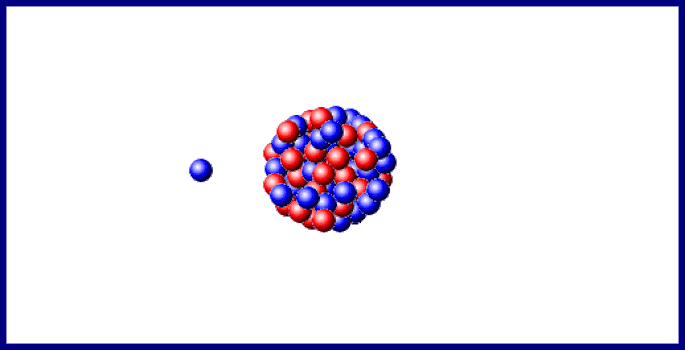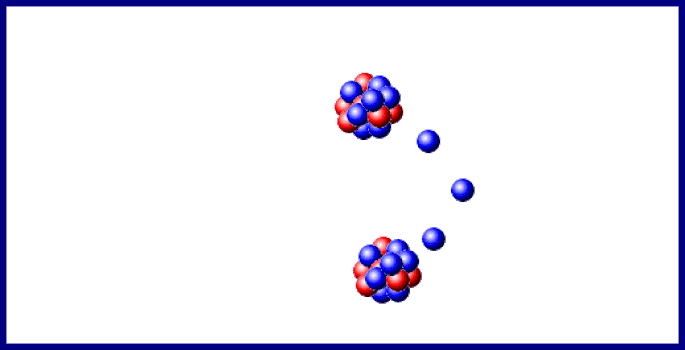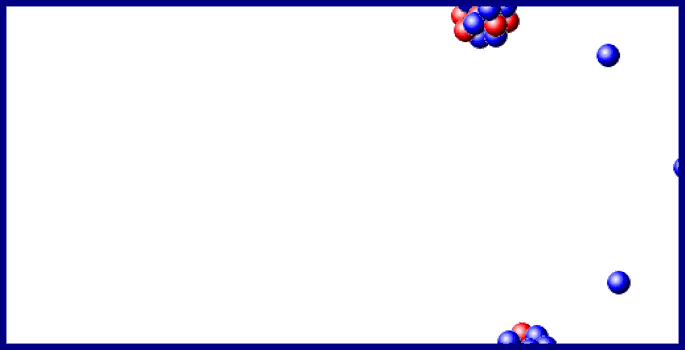
You should carefully examine the changes in both atomic number (protons) and mass number (protons plus neutrons): The earliest stages of the decay scheme involve only three elements, as shown in Figure 1. Review the first few steps in the decay of uranium‐238, which changes to lead‐206 after the emission of eight alpha and six beta particles. The most familiar radioactive element is uranium, which has two naturally occurring isotopes of mass numbers 235 and 238 that decay very slowly. The atomic number increased to 83 due to the new proton, but the mass number stayed constant because both metal nuclei have 212 total protons plus neutrons. An example of beta transmutation is the decay of lead‐212: The creation of the proton causes the atomic number to increase by one. The beta particle arises from the decay of a neutron to a proton: The beta particle can be denoted as an electron (e –) or with the Greek letter beta ( ). The other chemically important mode of radioactive transmutation is provided by negative beta particles (β), which are electrons emitted by atomic nuclei, not from the surrounding electronic orbitals. This is also true for the total charge on each side. Also notice that the total of the mass numbers on each side are the same, indicating they are conserved. Notice that radioactive decay actually changes one chemical element to another element, a process referred to as transmutation. The decay of thorium‐232 provides an example: If an unstable nucleus emits an alpha particle, its atomic number decreases by 2 and its mass number decreases by 4. The number of protons identifies the chemical element, whereas the nucleon total is the mass number for the particle or isotope. This nuclear notation uses a subscript to the lower left to record the number of protons, whereas the superscript to the upper left is the mass number, the total number of nucleons.

An alpha particle (α) is a nucleus with 2 protons and 2 neutrons. The atomic mass shown on the periodic table is the mass number of the most common isotope of each radioactive element.įor chemical purposes, the most important types of radiation are alpha and beta particles. Radioactivity, the spontaneous disintegration by the emission of particles. Such large nuclei are unstable and undergo
If you look at the periodic table, you will notice that all elements after bismuth, atomic number 83, have their atomic mass denoted by an integer within parentheses. Quiz: Introduction to Oxidation-Reduction Reactions.Introduction to Oxidation-Reduction Reactions.Quiz: Heat Capacities and Transformations.Quiz: Introduction to Organic Compounds.Quiz: Compounds with Additional Elements.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
